In forex trading, understanding different order types is essential for executing smart strategies and managing risk. One such order type is the sell stop, often used by traders who expect the market to continue falling once a specific price level is breached.
But what does a sell stop mean in forex? How is it different from a sell limit or a market order? In this article, we’ll break down the concept of the sell stop order, explain how it works, and show you when and how to use it effectively.
What is a Sell Stop?
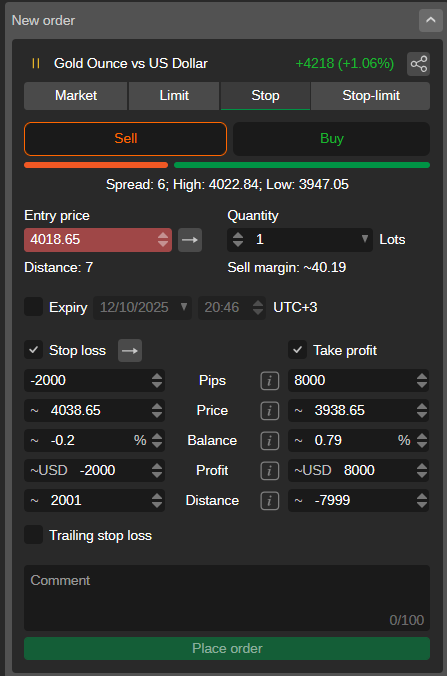
A sell stop is a pending order used in forex and other markets. It instructs your trading platform to sell an asset once its price drops to or below a specific level, which is lower than the current market price.
In simple terms:
You use a sell stop when you believe that if the price falls to a certain level, it will continue falling further, and you want to automatically enter a short position at that moment.
For example, if EUR/USD is currently trading at 1.1000, and you believe that if it breaks below 1.0950 it will drop further, you might set a sell stop order at 1.0950. Once the market reaches that price, your sell stop is triggered and becomes a market order, selling at the next available price.
Key Characteristics of a Sell Stop Order:
-
- It is placed below the current market price.
- It becomes a market order once the price is hit.
- It is used to enter a trade, not just to exit.
- Commonly used in breakout or trend-following strategies.
How Does a Sell Stop Work in Forex Trading?
A sell stop order in forex is a tool that traders use to automatically enter a short position if the price of a currency pair falls to a certain level. This order is not executed right away. Instead, it stays pending until the market price drops to the level you’ve set. Once the price hits that level, the sell stop is triggered and becomes a market order, meaning it will sell at the next available price.
For example, imagine the EUR/USD is currently trading at 1.1000. You believe that if the price falls to 1.0950, it will continue to drop further. So, you place a sell stop at 1.0950. As long as the price remains above that level, your order just sits there. The moment the market reaches 1.0950, your broker executes the sell order, putting you into a short position.
The purpose of a sell stop is to catch downward momentum. It’s used when you don’t want to enter a trade until the market shows a sign of weakness, specifically, by breaking through a certain price floor. This is different from placing a sell order at the current market price, where you’re jumping in immediately.
It’s important to understand that you must place a sell stop below the current market price. If you try to set it above the current price, the system won’t allow it, that would be a different kind of order called a sell limit.
Also, when a sell stop is triggered, you’re not guaranteed to get filled at the exact price you specified. In fast-moving markets, you might get a slightly lower price due to slippage. That’s something all traders should be aware of, especially during high-impact news releases or low-liquidity sessions.
In short, a sell stop helps traders automate their entries into short trades when they expect the market to drop below a certain level and keep falling.
Sell Stop vs Sell Limit
Many traders confuse a sell stop with a sell limit, but they are two very different types of orders used in completely different situations.
A sell stop is used when you want to sell below the current market price. The logic is simple: if the price falls to a certain level, it might continue falling. You want to catch that downward movement by entering a short position as the price breaks lower.
On the other hand, a sell limit is used when you want to sell above the current market price. This is for situations where you think the price will rise to a certain level, hit resistance, and then start falling. You’re selling high, expecting a reversal — not a breakout.
To summarize:
-
- Sell Stop: Used to enter a short trade below the current price. You expect the price to fall further.
- Sell Limit: Used to enter a short trade above the current price. You expect the price to rise, then reverse downward.
For example, if GBP/USD is trading at 1.3000:
-
- A sell stop might be placed at 1.2950, you think a break below that means more downside is coming.
- A sell limit might be placed at 1.3050, you think the price will rise to that level, then drop.
Understanding the difference is important. Using the wrong order type can lead to entering trades at the wrong time or missing setups entirely.
Sell Stop Example
To make the concept of a sell stop clearer, let’s walk through a simple example using a real trading scenario.
Suppose the USD/JPY currency pair is currently trading at 150.80. After analyzing the chart, you notice a strong support level around 150.50. You believe that if the price breaks below this support, it could trigger further selling pressure and continue downward.
Instead of entering a short trade immediately, you decide to wait for confirmation. You place a sell stop order at 150.48, just below the support level. Your logic is that if the price drops to 150.48, it’s likely that the downward trend will continue.
While the price remains above 150.48, your order is inactive. But as soon as the market drops and touches that price, your sell stop order is triggered. It becomes a market order and is executed at the next available price — which could be 150.48 or slightly lower depending on market conditions.
Once the order is filled, you’re in a short position, and you’re now expecting the price to continue moving lower. You might also place a stop loss above the broken support to manage your risk in case the move turns out to be a false breakout.
This kind of setup is common for breakout traders who don’t want to guess tops or bottoms but prefer to enter when the market shows a clear move in one direction.
Why Use a Sell Stop Order?
Traders use sell stop orders for a few key reasons, mostly related to strategy and discipline. One of the main reasons is to catch downward breakouts. Instead of trying to guess when the market will turn, traders wait for confirmation that the price is already moving in their expected direction — in this case, downward. A sell stop lets them automatically enter a short trade if the price drops to a certain level.
Another reason to use a sell stop is to remove emotion from trading. By setting the order in advance, you’re sticking to your plan rather than reacting impulsively to live market movement. It helps you stay disciplined and consistent, especially if you’re not actively watching the charts all the time.
Sell stops are also useful in fast-moving markets. When big economic news is expected, prices can move quickly. With a pending order like a sell stop already in place, you don’t need to rush to enter the trade manually — the platform will execute it for you the moment your conditions are met.
Here are a few common situations where traders use sell stops:
-
- To enter short trades when price breaks below support
- As part of breakout or trend-following strategies
- To automate entries during news events
- To avoid manually monitoring the market for a setup
Sell stops are mainly for entering new trades, but they can also be used to exit existing long positions in some trading platforms — acting like a stop-loss. However, in this article, we’re focusing on their use as entry orders.
Can You Place a Sell Stop Above Market Price?
One common point of confusion for beginners is whether a sell stop can be placed above the current market price. The short answer is: no, you cannot.
A sell stop order is specifically designed to be placed below the market price. It only becomes active when the price falls to that level. If you try to place a sell stop above the market, most trading platforms won’t allow it — because it doesn’t match the logic of how a sell stop works.
Let’s say the current price of EUR/USD is 1.1000. If you try to set a sell stop at 1.1050 (which is above the market), it wouldn’t make sense. Why? Because a sell stop is used when you expect the price to drop, not rise. If you think the price will go up and then reverse downward, you’d be looking at a sell limit order, not a sell stop.
Traders use sell stop orders to catch downward momentum. Placing it below the current price means you’re waiting for the market to show weakness — for example, breaking a support level. Once that level is hit, the order is executed, and you’re entered into a short position automatically.
In short, a sell stop above market price doesn’t work, it goes against how this order type functions in forex trading.
Conclusion
A sell stop is a powerful tool in forex trading that allows traders to enter short positions automatically when the price drops to a specific level. Instead of jumping in early, you can wait for the market to confirm your idea by breaking a key support level, and let your sell stop order handle the entry.
It’s important to remember that a sell stop is always placed below the market price, and once triggered, it becomes a market order. This makes it useful in breakout strategies, trend-following setups, and situations where you want to automate your trades and remove emotions from the decision-making process.
Whether you’re new to forex or looking to improve your order placement, understanding how sell stop orders work is essential. It helps you enter trades more strategically and manage risk with greater control.
Like any trading tool, it’s best to practice using sell stops in a demo account first. That way, you can see how they behave in real-time conditions without risking real money.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a sell stop in forex?
A sell stop in forex is a pending order placed below the current market price. It triggers a sell market order once the price reaches that level, allowing traders to enter short positions during downward price moves.
What does sell stop mean?
A sell stop means you want to sell an asset only after its price falls to a specific level, expecting the price to continue dropping.
When is a sell stop order executed?
A sell stop order is executed in the market as soon as the price hits or falls below the stop price you set.
Can a sell stop be placed above market price?
No. A sell stop must be placed below the current market price. If you want to sell above market price, you need to use a sell limit order instead.
What is the difference between a sell stop and a sell limit?
A sell stop is placed below the current market price to catch downward breakouts. A sell limit is placed above the market price to sell when the price rises to a resistance level and then reverses.