In trading, there are two major approaches to analyzing market direction: trend-following strategies and counter-trend strategies. Both aim to take advantage of price movements, but they differ completely in how traders interpret market trends and decide when to enter or exit a trade.
A trend-following strategy focuses on trading in the direction of the prevailing market movement, buying when the market is rising and selling when it’s falling. It’s based on the idea that “the trend is your friend,” meaning once a strong trend is established, it often continues for some time.
On the other hand, a counter-trend strategy is built on anticipating reversals. Traders using this method look for signs that a current trend is losing strength and attempt to profit from corrections or complete trend changes. This approach is often more complex and requires strong timing, risk control, and understanding of market psychology.
Whether you trade forex, crypto, or stocks, understanding the differences between trend-following and counter-trend methods is essential. Each strategy offers unique opportunities, one thrives on momentum, the other on reversal points. The key is knowing when to apply each one.
What Is a Trend-Following Strategy
A trend-following strategy is based on the idea of aligning trades with the dominant direction of the market. When prices are moving consistently upward, traders look for buying opportunities, and when the market is trending downward, they look to sell or short. The main principle is to follow the established momentum rather than predict reversals.
These strategies rely on technical analysis and the use of trend-following indicators that help identify the direction and strength of a trend. Tools like moving averages, RSI, and MACD are commonly used to confirm momentum and define entry and exit points. Traders aim to capture large portions of market moves while avoiding minor fluctuations.
Trend-following is one of the most popular approaches among beginners and experienced traders alike because it provides a clear framework and simple rules. It is especially effective in markets that tend to form long, steady trends, such as major forex pairs or cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
Ultimately, the goal of a trend-following strategy is to stay in profitable trades as long as the trend remains intact and to exit when signs of reversal appear.
Examples of Trend-Following Strategies
There are several practical ways to apply trend-following strategies, each designed to capture movement in the direction of the prevailing trend. The most common include breakout trading, pullback entries, and moving average systems.
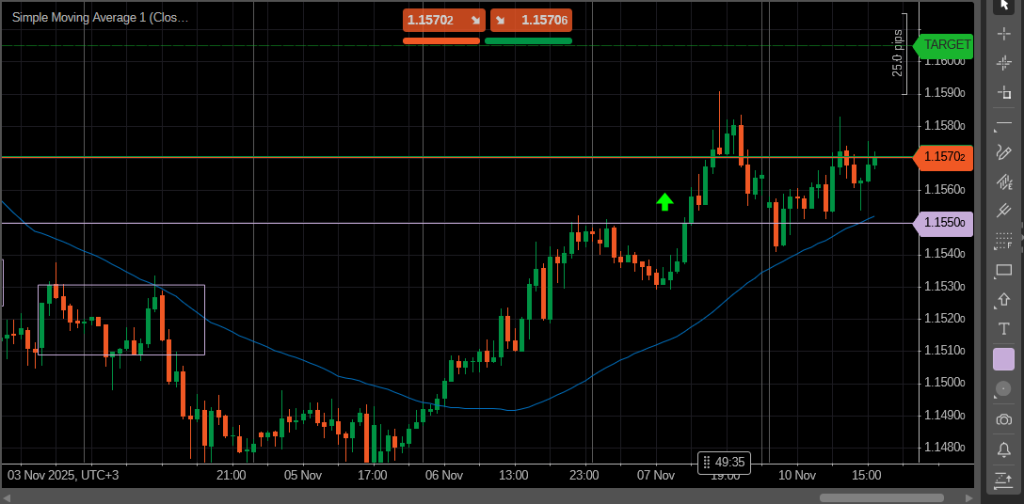
A breakout trading strategy focuses on entering the market when the price breaks through a significant resistance or support level. The logic behind this setup is that once the price escapes a range, it often continues in that direction with strong momentum.
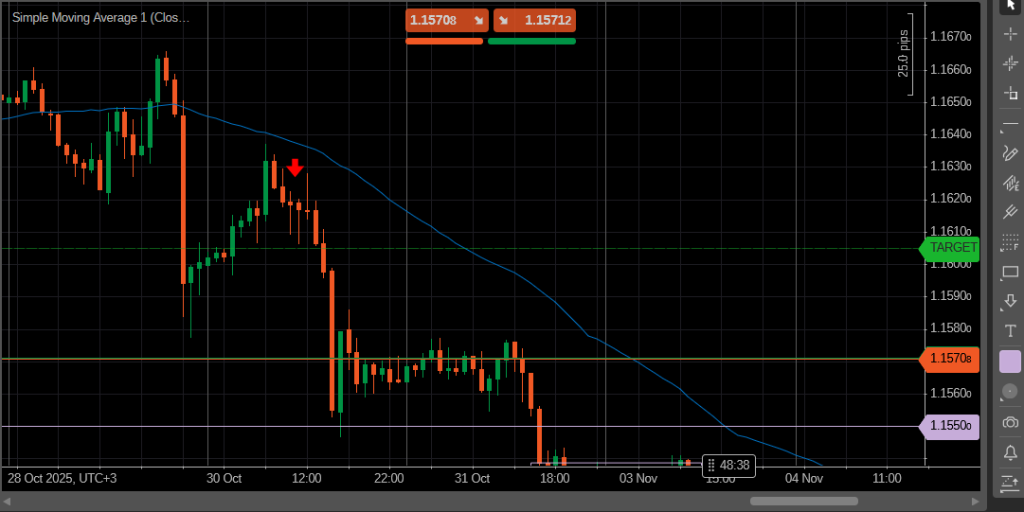
A pullback entry strategy, on the other hand, waits for a temporary correction within a trend. Traders look for retracements toward key moving averages or previous resistance-turned-support levels to enter in the direction of the main move. This approach often offers a better risk-to-reward ratio compared to chasing the trend.
Moving average systems are another common trend-following method. Even a simple trend following strategy using a single moving average, like the SMA50, can help identify when the market stays above or below its dynamic level. Combined with other indicators, it provides clear trend direction and timing for entries and exits.
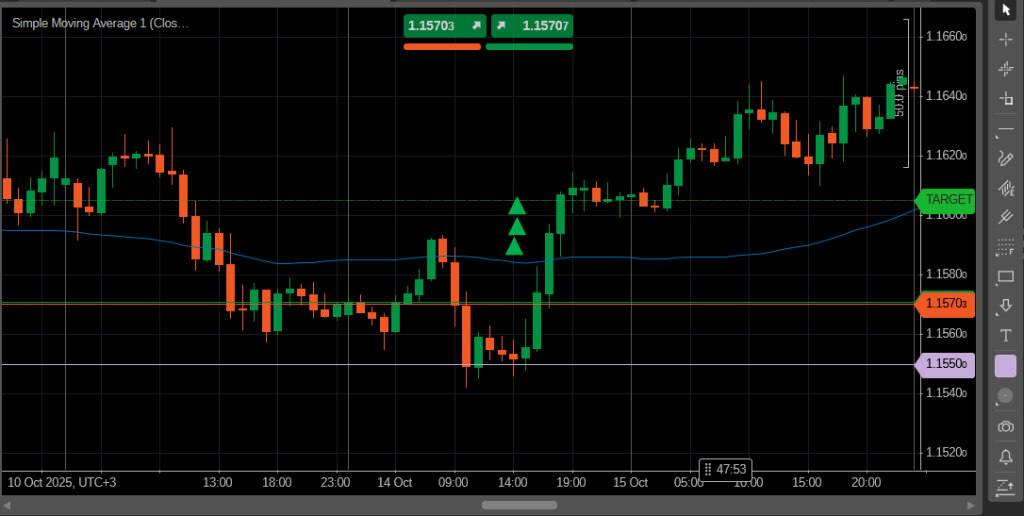
To improve results, traders often use defined trend following strategy rules that outline how to enter, manage, and exit trades. They also evaluate performance through backtesting to estimate the trend following strategy win rate under different market conditions.
Trend-Following in Different Markets
Trend-following strategies can be applied across multiple markets, including forex, cryptocurrencies, commodities, and indices. However, each market has its own behavior, volatility, and timing, which influences how these strategies are used.
In forex trading, trend-following strategies often rely on higher timeframes to capture long and steady moves driven by economic cycles and central bank policies. Popular forex trend following strategies involve identifying clear price swings and using moving averages or breakout confirmations to ride strong currency trends.
In the crypto market, volatility creates both opportunity and risk. A trend following strategy for crypto can work well when digital assets, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, enter long directional moves after consolidation phases. Many investors use trend following strategies for crypto investors to stay aligned with market momentum while applying strict risk control.
Day traders may prefer short term trend following strategies that focus on intraday moves during high-liquidity sessions. These setups usually rely on momentum indicators and short-term breakouts. Backtesting remains crucial to evaluate consistency and adjust parameters before applying them in live conditions.
No matter the market, the essence of a trend-following approach stays the same — follow the trend until it ends. What changes is the timeframe, volatility, and the tools chosen to identify opportunities effectively.

What Is a Counter-Trend Strategy
A counter-trend strategy takes the opposite approach to trend-following. Instead of joining an ongoing trend, it aims to identify moments when the current market direction is likely to pause, correct, or reverse. Traders using this method believe that no trend moves in a straight line forever, and that price often retraces before continuing or changing direction entirely.
The concept behind a counter-trend move is to profit from these temporary pullbacks or full reversals. For example, if the market has been rising for several sessions, a counter-trend trader might look for overbought signals or reversal candlestick patterns near resistance levels to enter a short trade. Similarly, after a strong decline, they might buy when the market shows signs of exhaustion near key support.
This approach requires patience and precision, as counter-trend strategies go against the prevailing market momentum. Timing errors can quickly lead to losses if the trend resumes with force. Because of this, many traders rely on oscillators such as RSI or Stochastic to detect overextended price conditions and confirm entry signals.
While counter-trend trading can be riskier, it often provides excellent reward-to-risk setups when applied correctly. The goal is to identify when the market’s energy is fading and capitalize on the reaction before the next major move begins.
Counter-Trend Strategy Examples
Counter-trend strategies can take many forms, but they all share one principle — entering trades when the market shows signs of exhaustion or overextension. These setups aim to capture retracements or full reversals before a new move develops.
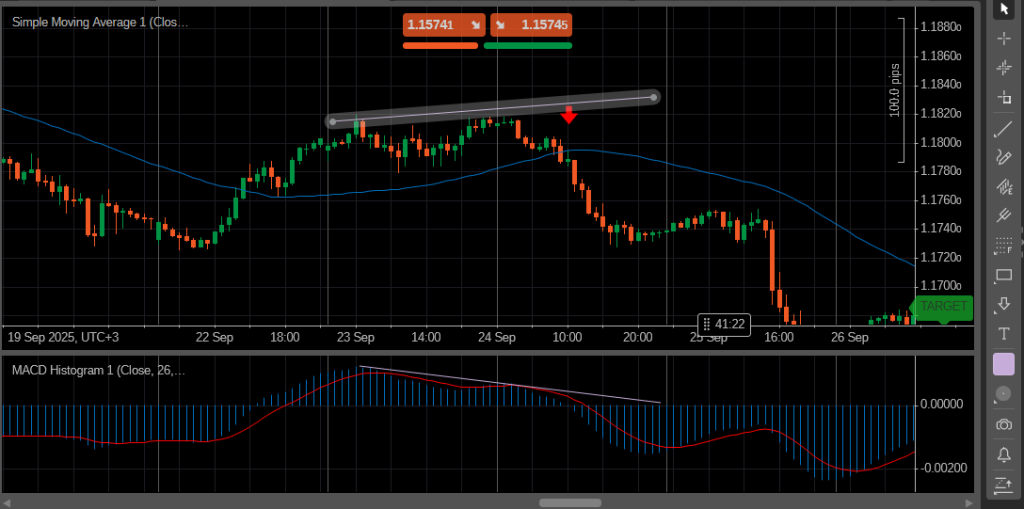
One of the most common counter-strategy examples is divergence trading. This occurs when price forms a new high or low, but an oscillator like the RSI or MACD fails to confirm the move. Such divergence often signals a weakening trend and a potential reversal, making it a classic counter-trend setup.
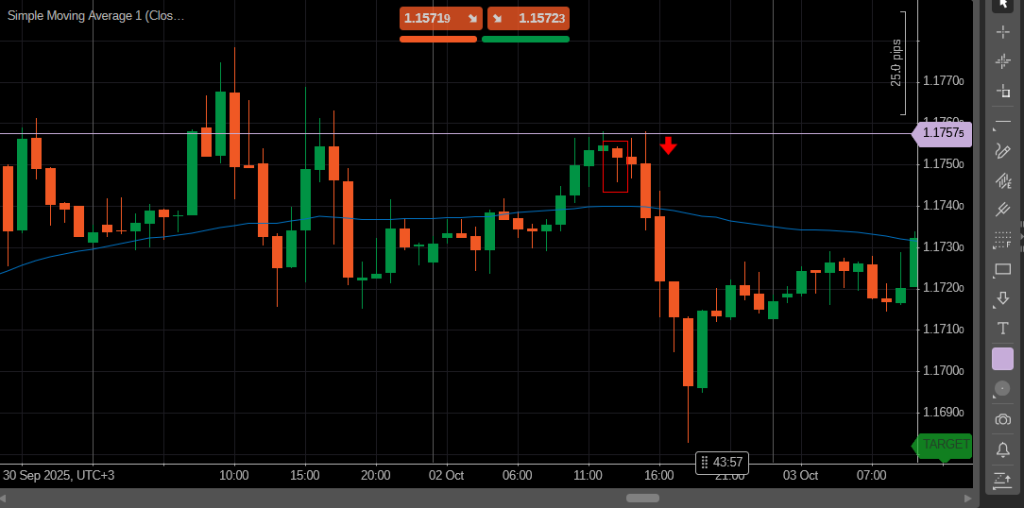
Another example involves trading around key support and resistance zones. When the price reaches a historically strong area and shows rejection signals, traders anticipate a reversal. Candlestick formations such as pin bars, engulfing patterns, or tweezer tops and bottoms often confirm these counter-trend opportunities.
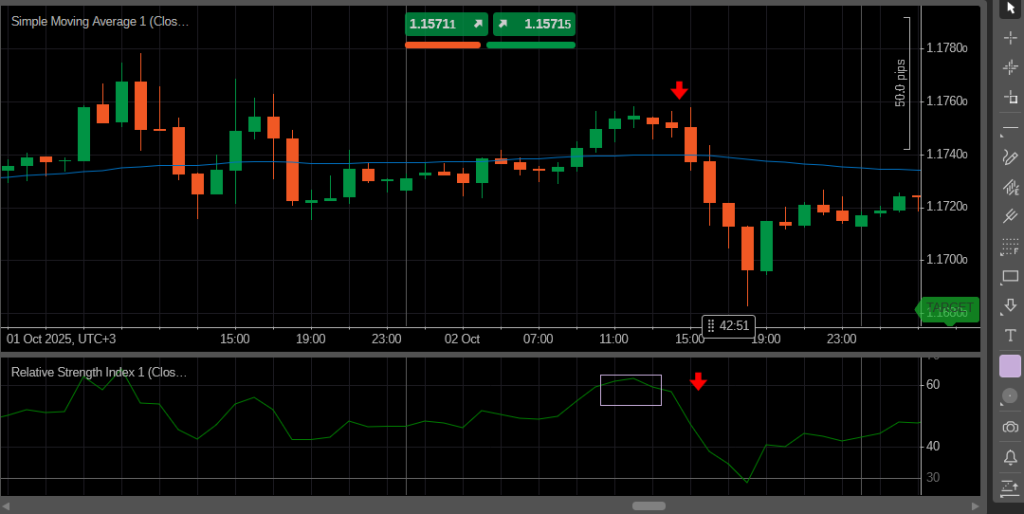
A third approach uses overbought or oversold indicators. When a market becomes extremely stretched in one direction, counter-trend traders enter against the move, expecting a short-term correction. This method is frequently used in forex and crypto markets, where strong momentum phases are followed by sharp retracements.
Regardless of the method, managing risk is essential. Counter-trend moves can quickly fail if the dominant trend resumes, so traders often use tight stop-loss levels and clear exit rules to protect capital.
Pros and Cons of Each Approach
| Aspect | Trend-Following Strategies | Counter-Trend Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Main Idea | Trade in the direction of the prevailing market movement. | Trade against the current trend to catch reversals or corrections. |
| Market Condition | Works best in strong, trending markets. | More effective in ranging or overextended markets. |
| Entry Logic | Enter on breakouts, pullbacks, or confirmed momentum. | Enter when price shows exhaustion or reversal signals. |
| Indicators Used | Moving averages, MACD, RSI, ADX. | RSI, Stochastic, divergence, support/resistance levels. |
| Advantages | High consistency in strong trends, simple rules, clear direction. | High reward-to-risk potential, opportunities in sideways markets. |
| Disadvantages | Whipsaws in flat markets, possible late entries. | Higher failure rate, requires precise timing and strict risk control. |
| Risk Profile | Generally lower risk when trend is stable. | Higher risk due to trading against momentum. |
| Trader Type | Suited for traders who prefer to follow momentum and stay in longer moves. | Preferred by traders who like short-term corrections and fast reversals. |
| Example Setup | Trend following breakout strategy, pullback entry, SMA-based system. | Divergence trading, reversal at support/resistance, overbought/oversold entries. |
| Key to Success | Patience to stay with the trend and avoid early exits. | Accurate timing and tight stop-loss management. |
Choosing Between Trend-Following and Counter-Trend
Selecting between trend-following and counter-trend approaches depends on a trader’s style, experience level, and how they interpret market conditions. Both can be profitable, but they require different mindsets and techniques.
Traders who prefer structure, patience, and clarity often lean toward trend-following strategies. These methods work best when markets display strong directional momentum. Using a reliable trend following strategy indicator, such as the SMA50 or ADX, helps confirm the dominant direction and filter out false signals. Trend-following suits those who aim to capture larger moves rather than frequent small profits.
Counter-trend strategies appeal to traders who enjoy identifying turning points and taking advantage of market overreactions. A proper counter-trend setup includes clear rejection patterns, momentum slowdown, and strong confirmation before entry. Because this method involves higher risk, it’s essential to apply disciplined stop-loss placement and defined exit points.
Many traders successfully combine both styles — following the trend on higher timeframes while using counter-trend signals on shorter ones to fine-tune entries or exits. This hybrid approach allows more flexibility and adaptability to changing market conditions.
In all cases, proper trade management and strategies for closing sales are crucial. Whether following momentum or fading it, every trader must know when to exit, lock in profits, or cut losses quickly.

Conclusion
Both trend-following and counter-trend strategies offer unique ways to approach the market. Trend-following focuses on staying with the dominant direction, capturing profits as long as momentum remains strong. Counter-trend strategies, in contrast, look for moments when that momentum weakens, aiming to profit from reversals or temporary corrections.
Choosing the right approach depends on your trading style, time availability, and risk tolerance. Some traders prefer the stability and structure of trend-following, while others thrive on the faster opportunities that counter-trend setups provide. Both can be effective when supported by solid risk management and emotional discipline.
Before applying either strategy in real conditions, traders should always test their methods. Backtesting and demo trading help determine how well a strategy performs under different market environments. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both sides, traders can build a well-balanced system that adapts to any market phase.
Ultimately, the goal is not to pick sides but to recognize when each approach is more suitable. Market conditions constantly change, and a flexible trader who knows how to combine trend-following with counter-trend insights can take advantage of both momentum and reversal phases.
FAQ
What is a trend-following strategy?
A trend-following strategy is a trading approach that focuses on entering trades in the direction of the prevailing market movement. Traders use indicators like moving averages or MACD to confirm the trend and hold positions as long as momentum remains strong.
What does a counter-trend strategy mean?
A counter-trend strategy involves trading against the current market direction to profit from reversals or short-term corrections. It aims to identify moments when a trend is losing strength and price is likely to change direction.
Which strategy is safer — trend-following or counter-trend?
Trend-following is generally considered safer because it aligns with market momentum. Counter-trend trading can be riskier since it goes against the dominant force, but it can offer higher potential returns if timed correctly.
Can I use both strategies together?
Yes, many traders combine both approaches. For example, they may use a trend-following strategy to determine market direction and a counter-trend setup for fine-tuning entries or exits.
What indicators are best for trend-following?
Common trend following strategy indicators include moving averages (such as SMA50), ADX, and MACD. These help identify trend strength and direction.
What indicators work best for counter-trend strategies?
Counter-trend traders often rely on oscillators like RSI or Stochastic to detect overbought or oversold conditions, as well as divergence between price and momentum.
Which strategy works better in forex trading?
Both can work effectively in forex trading. Trend-following strategies tend to perform better during strong directional phases, while counter-trend strategies are useful when the market consolidates or becomes overextended.
Do these strategies work for crypto as well?
Yes. Trend-following strategies for crypto investors work well during strong bullish or bearish phases, while counter-trend strategies can capture short-term corrections in volatile markets.
How can I improve my strategy’s success rate?
Consistent backtesting, disciplined risk management, and adapting to market conditions are key. It’s also important to define clear trend following strategy rules or counter-trend setup conditions before trading live.